Introduction
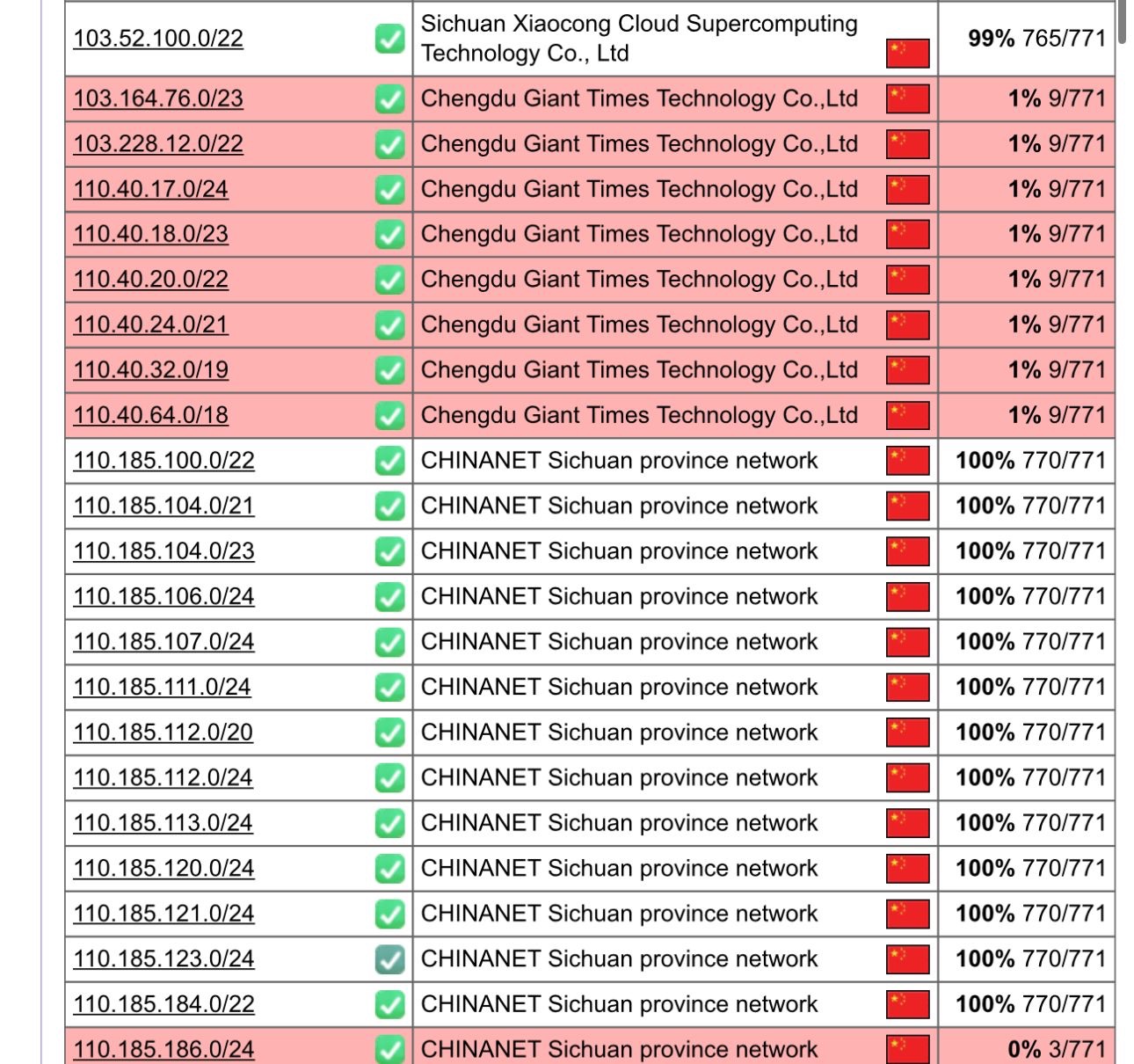
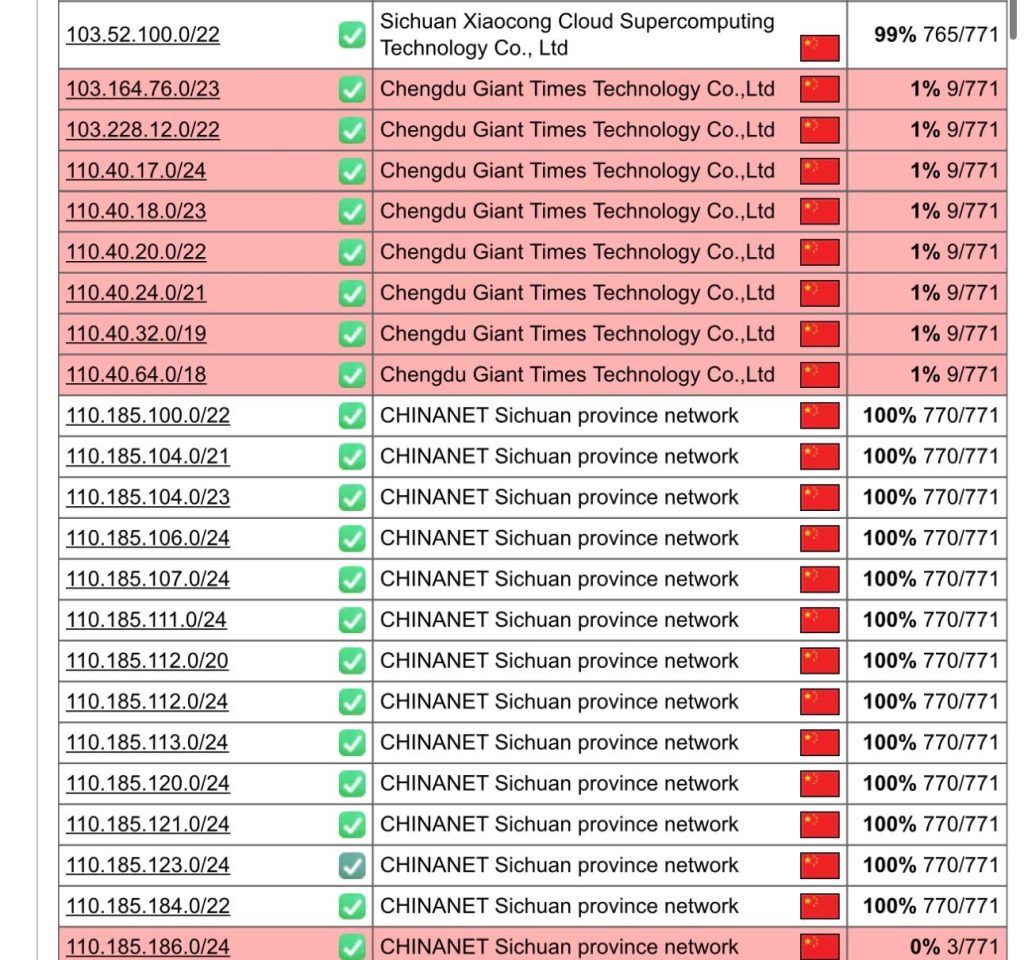
On September 4, 2025, multiple data centers in Chengdu, Sichuan Province, experienced a large-scale network interruption, resulting in the complete disconnection of the 110.40.x.x IP segment. This incident arises from a severe debt dispute between the upstream provider, Chengdu Netke Juli Times Company, and Sichuan Telecom Group, causing operational halts for numerous low-cost server providers and drawing significant industry attention. Such unexpected infrastructure failures highlight potential risks in telecommunications debt management and impose direct economic losses on reliant businesses and users.
Event Background and Causes
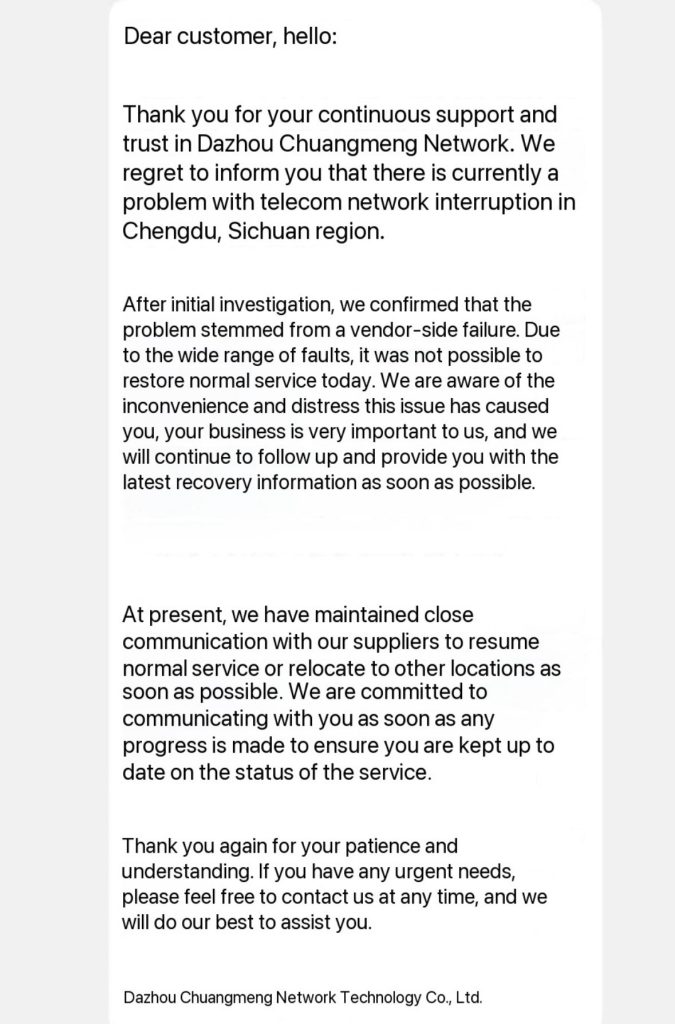
According to reliable sources, Chengdu Netke Juli Times Company serves as the upstream network provider for several data centers, including Guanghua, Aofei, Zhongli, and Dayi, and has accumulated substantial long-term debts with Sichuan Telecom Group that it has been unable to repay promptly. Consequently, Sichuan Telecom terminated IDC (Internet Data Center) network access services for the company on September 4, 2025, directly leading to the interruption of associated network lines. The company’s official statement underscores that this outcome was not anticipated and expresses regret for the impact on affected users. However, this decision has quickly propagated to downstream providers, with many low-cost server vendors active on platforms such as LowEndTalk (LOC) facing operational challenges due to their reliance on Chengdu’s infrastructure. These vendors typically attract clients through cost advantages, but the event underscores vulnerabilities in the supply chain.
Scope of Impact and Potential Consequences
The outage primarily affects the server hosting and cloud services market in the Chengdu region. Initial assessments indicate that impacted vendors include multiple entities offering virtual hosting, VPS, and dedicated servers, with user groups encompassing small and medium-sized enterprises, individual developers, and cross-border e-commerce platforms. Additionally, it is understood that the study abroad industry giant, Liuxuesheng Net (https://www.lxs.net), also has services deployed in the relevant data centers, and as of the time of publication, it has not fully restored the related services. Service disruptions may result in data loss, inaccessible websites, and delayed responses, potentially triggering chain reactions such as contract breaches and customer attrition. Industry experts note that, amid accelerating digital transformation, such incidents not only amplify economic damages but may also erode confidence in domestic data centers, prompting some operations to relocate to other regions. Furthermore, the public disclosure of the debt dispute could prompt regulatory intervention, encouraging enhanced financial oversight and risk management protocols in the telecommunications sector.
Industry Reflections and Response Recommendations
This incident is not isolated but reflects a broader pattern of debt issues within telecommunications infrastructure. In recent years, intensified market competition and economic pressures have led to frequent similar disputes. To mitigate such risks, it is recommended that relevant enterprises and users adopt the following measures: first, diversify supplier selections to avoid over-reliance on a single region or provider; second, strengthen contract clause reviews to ensure compensation mechanisms for service interruptions; third, implement real-time network monitoring and prepare contingency plans, such as multi-site backups or cloud migration strategies. At the regulatory level, efforts should focus on promoting debt transparency and early warning systems to safeguard industry stability.
Conclusion
The Chengdu data center outage serves as a reminder that the reliability of telecommunications infrastructure is foundational to the digital economy. It is hoped that through prompt negotiations and solutions, all affected parties can restore normal operations expeditiously. This event also calls for collaborative efforts across the industry to build a more resilient network ecosystem. For further details, please monitor subsequent official updates.